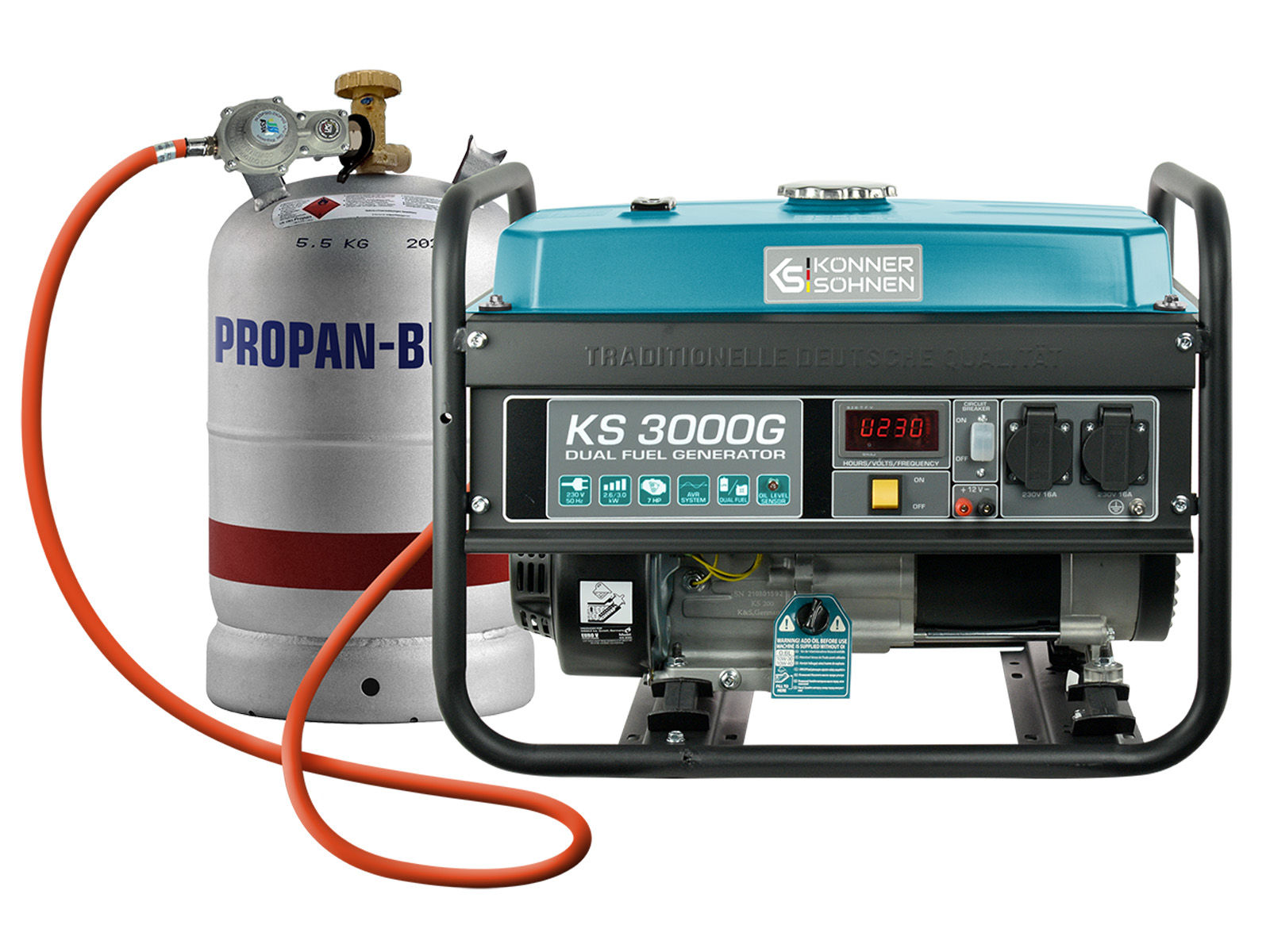
Modern society moves towards flexibility and renewable energy.
Power island solutions and power supply systems with batteries have become a trend and are becoming more and more common. We are currently experiencing rapid changes in the manufacture of batteries and accumulators, which are increasingly affecting our everyday lives.
Electricity storage devices are increasingly becoming part of different power supply systems. Solar systems, wind turbines, electric cars, household appliances with rechargeable batteries, computer systems with UPSs, telecommunications, surveillance systems, etc. are equipped with long-life batteries.
The batteries are charged from either an AC or DC power source. However, the AC voltage must first be rectified, which is a technical problem in itself at higher power levels.
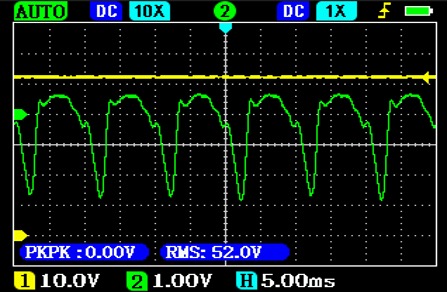
Most AC/DC chargers and also charging modules in the inverters have a pulsed power consumption and most of them charge the battery storage device in a pulsed manner:
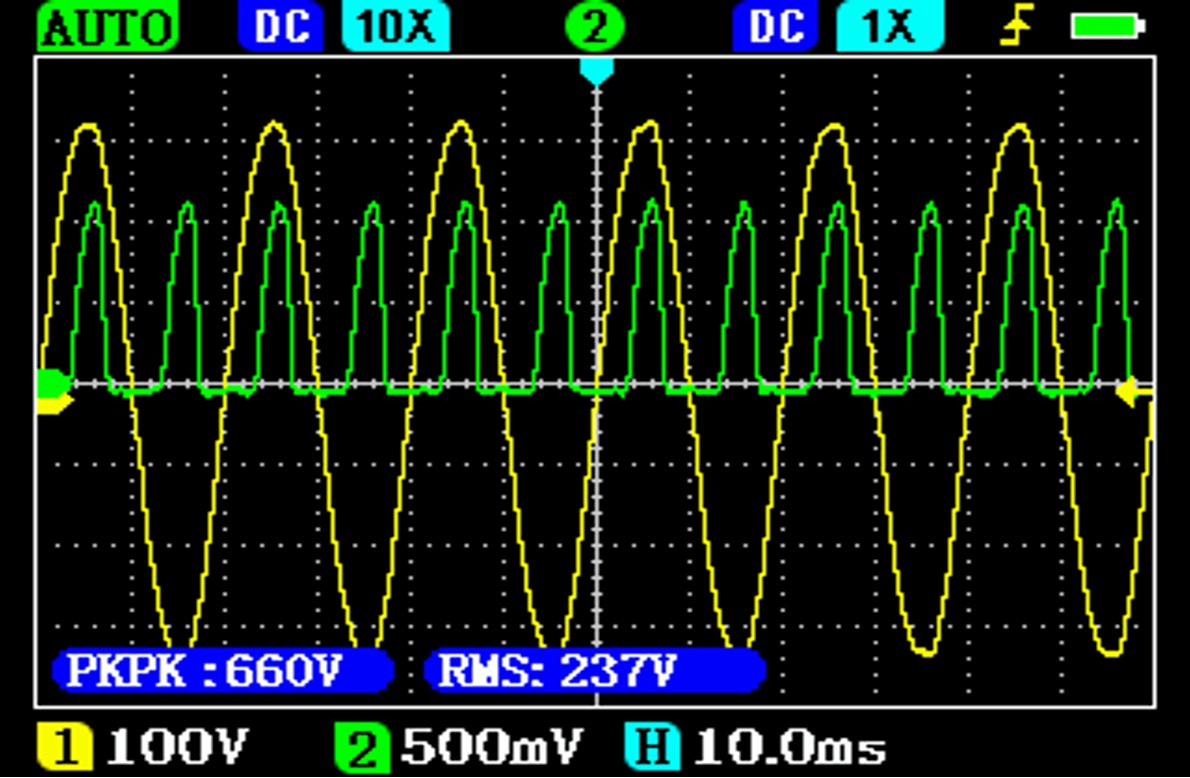
Current consumption (green) of the charger
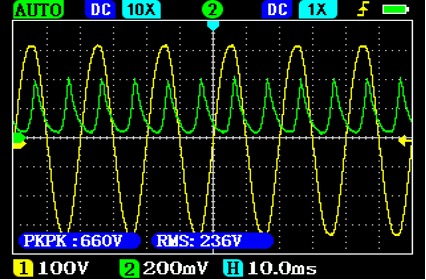
Charging current (green) of the battery
The mains voltage is shown in yellow. In the case of chargers or charging modules without power factor correction, only the maxima of the sine wave are consumed.
Pulse current consumption has a power factor of 0.5-0.6, which causes high reactive power. When operating from the public power grid, there are fewer problems because several power consumers run in parallel and balance each other out.
When using an AC generator, however, various technical problems arise, which mean that you cannot use more than half of the nominal power of the generator and measures must be taken to stabilize the circuit against the harmonics caused by pulse-like current consumption.
In practice, it often leads to unstable operation of the charger and even damage to the generator such as overheated windings, broken voltage regulator or inverter module.
A conventional generator must not be used as a backup power source for a UPS or an inverter, since the charging module can distort its voltage, which in turn affects the electricity consumers to be supplied. Generators with inverter technology are better suited for this, but you have to reckon with limitations in performance.
DC GENERATORS as an energy source for battery storage solve the problem in a different way and have a lot of advantages in that sense.
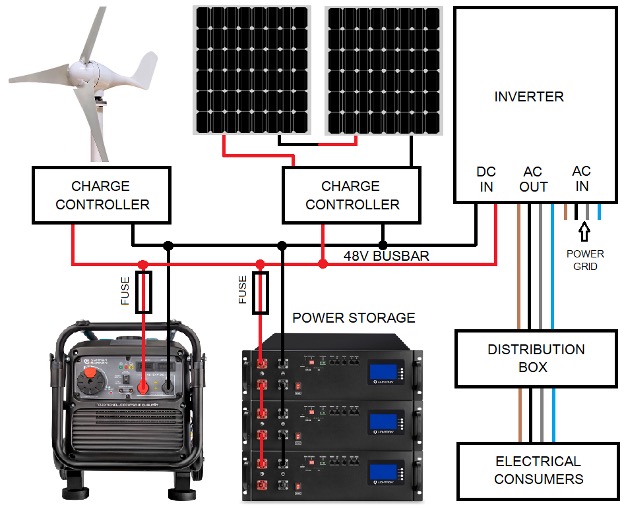
KS 48V-DC is connected directly to the battery or 48V busbar and performs the same function as other direct current sources such as a solar field or wind turbine with a charge controller.
Charging the battery via the solar charge controller is complicated, depending on the power consumption of the inverter:
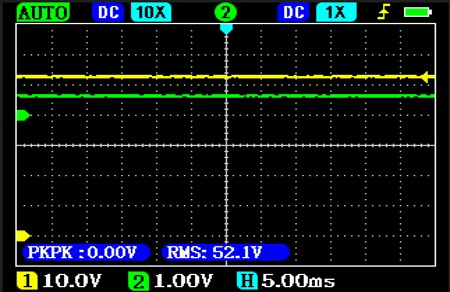
In the image on the left, no power is being drawn from the inverter to power the home and in the image on the right, the power is being drawn in pulses to create a sine wave.
The DC generator has multiple windings and electronic control, which makes the output current much smoother. This is how the charging current (in green) of a LiFePo4 battery (an extreme case) at 40A and 70A current (rms value) looks like:
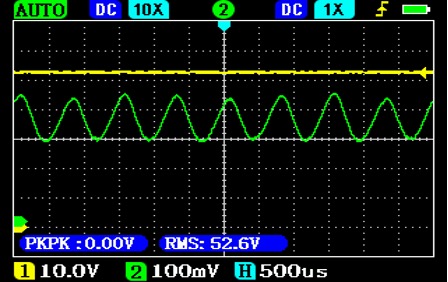
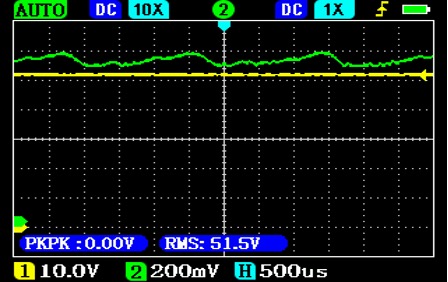
The DC generator output voltage ripple is very low, which can still cause charging current ripple in a LiFePo4 battery. As the charging current increases, the difference between the battery's own voltage and the generator's voltage increases, which can lead to a reduction in the charging current ripple.
A DC generator to charge the batteries is a good solution from all points of view and in some cases there is no better, if any, alternative.
For example, with on-grid inverters with backup power function and with a DC battery storage, there is no way to use an AC generator instead of the public power grid, since such a generator can be damaged by power feedback. The direct current battery storage can only be recharged from a direct current source.
Könner & Söhnen is always working on being able to offer our customers good solutions. A reliable power supply is extremely important and the DC generators from Könner & Söhnen should play an important role in this.
The KS 48V-DC direct current generator has been specially developed for 48V battery storage whose working voltage range overlaps with the 48-54V range.
Here are the parameters of the most common batteries in comparison:
State of charge | Voltage | Voltage | Voltage | Voltage | Voltage | Voltage |
100 | 54.4 | 51.0 | 58.0 | 53.9 | 52.0 | 50.4 |
90 | 53.2 | 49.9 | 56.7 | 53.1 | 51.0 | 50.0 |
80 | 53.0 | 49.7 | 55.4 | 51.9 | 50.0 | 49.7 |
70 | 52.8 | 49.5 | 54.1 | 50.7 | 49.2 | 49.3 |
60 | 52.6 | 49.3 | 52.8 | 49.5 | 48.6 | 48.8 |
50 | 52.5 | 49.2 | 51.5 | 48.3 | 48.2 | 48.2 |
40 | 52.3 | 49.1 | 50.2 | 47.1 | 47.8 | 47.6 |
30 | 52.0 | 48.8 | 48.9 | 45.8 | 47.2 | 47.0 |
20 | 51.6 | 48.4 | 47.6 | 44.6 | 46.6 | 46.3 |
10 | 48.0 | 45.0 | 46.3 | 43.4 | 46.0 | 45.2 |
It is imperative to pay attention to such parameters as maximum charging voltage, recommended current and usable capacity:
Charge | LiFePo4 | LiFePo4 | LiIon | LiIon | AGM | Blei-Säure |
Voltage, | 57.6 | 54.0 | 58.0 | 53.9 | 58.0 | 57.2 |
Current, | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
Usable | 90-100 | 90-100 | 90-100 | 90-100 | 50-80 | 50 |
The maximum output voltage of the KS 48V-DC is selected in such a way that no overcharging occurs, even with AGM and lead-acid batteries. This is in the area of trickle charging and cannot damage the batteries even if the generator runs for several hours.
If the voltage on the 48V bus bar is to rise to 57V (e.g. due to other DC power sources), the generator stops immediately, regardless of the mode.
The lithium batteries are equipped with BMS controllers, which also prevent overcharging.
The voltage range of 48-54V fits most 48V bus bars. The voltage drop in the cables from the generator to the 48V bus bars must also be taken into account, which can be 0.5-1.0V depending on the current strength.
The KS 48V-DC works like a charger or a charging module with an IU characteristic:
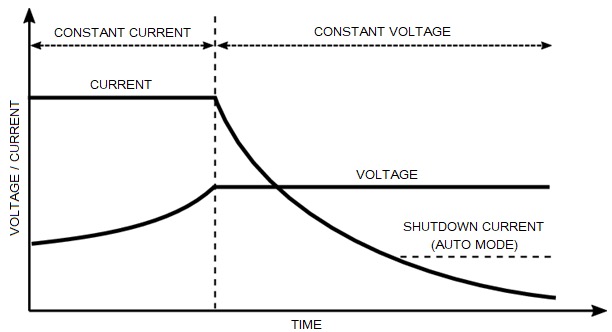
It performs the same function as any other DC source connected to the 48V bus, supplying power to the system when needed.
Different function algorithms can be implemented using the existing AUTO or EXTERNAL CONTROL mode. When choosing between AUTO and EXTERNAL CONTROL mode, the special features of the system to be supplied must be taken into account. When the generator is running and is the only source of DC power on the 48V bus, it takes over virtually all of the power supply, as its output voltage then remains slightly above the battery voltage.
If the average energy requirement is more than 50% of the nominal power of the generator (e.g. telecommunications systems), we recommend using several KS 48V-DC to increase the power:
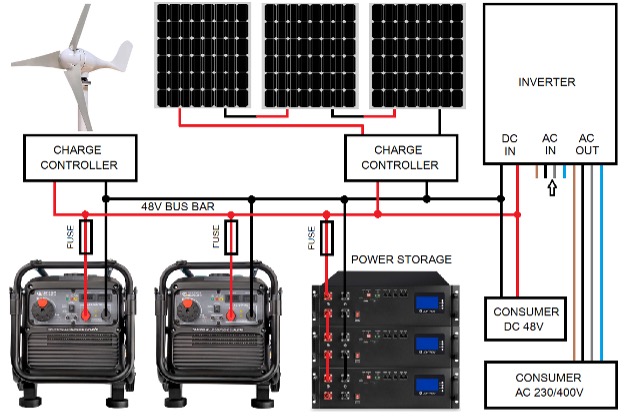
The total rated power of the DC generators connected in parallel should be at least twice higher as the average power consumption of the connected power consumers, so that uninterrupted operation can be guaranteed over the long term. For example, half of the DC generators can run while the other half can be cooled down, serviced or refueled.
In AUTO mode, such a system would also be self-regulating. Even a small deviation in the starting voltage of the generator means that the 1st generator starts first and the others come along when the battery voltage continues to drop if the output of the 1st generator alone is not sufficient. If the output current of one of the active generators falls below 20A, it is switched off within 30 seconds while the other generators continue to run.
If other direct current sources are to become active on the 48V busbar (charger module of the inverter or the UPS, AC/DC converter, charge controller of the PV modules or the wind turbine, etc.) and take over the power supply in part or in full, the current draw on the KS 48V-DC and when it is in AUTO mode, the controller shuts down the generator. If several KS 48V-DC are to run in parallel, they are switched off one after the other and only those continue to run where the current consumption exceeds 20A.
This saves fuel because the engine does not run at low loads but in the economical speed range.
In EXTERNAL CONTROL mode, the KS 48V-DC are only switched on and off via external potential-free “dry” contacts, except for overvoltage protection, which switches off the generator at 57V.
OPERATION IN AUTO MODE
The generator in AUTO mode monitors the voltage of the battery to be supplied and starts automatically when the lower voltage value of 47.5-48V is reached. Reaction time about 5 seconds.
The generator charges the battery with a voltage of up to 53.5-54V and a current of up to 70-75A and turns off as soon as the voltage reaches 53.5-54V and the charging current falls below 20A. Reaction time about 30 seconds.
The generator can be started by pressing the START button at any time regardless of the battery voltage, but will be stopped within 30 seconds after the current draw comes below 20A.
The green signal lamp (operating display) lights up continuously when the current draw exceeds 20A and flashes when the current draw falls below 20A.
If the power consumption in the respective case is technically never to fall below 20A (48V busbar), the EXTERNAL CONTROL mode should be used so that the generator does not run continuously.
OPERATION IN EXTERNAL CONTROL MODE
The generator in EXTERNAL CONTROL mode will be started by closing the CONTROL TERMINAL contacts and stopped by opening them. This mode allows the generator to be optimally adapted to different battery storage systems by external control of devices with potential-free “dry” contacts, which significantly expands the generator's range of application. With the jumper between the CONTROL TERMINAL contacts, the generator starts immediately as soon as the rotary switch is turned to the ON position and stops when it is in the OFF position. Such use is recommended in order to be able to start and stop the generator manually regardless of the battery voltage.
Many devices are equipped with potential-free “dry” contacts (inverters, UPSs, batteries with BMS controllers, battery monitors, time relays, etc.) and this allows to implement all possible algorithms of generator use.
OVERVOLTAGE and OVERLOAD PROTECTION
If the voltage on the 48V busbar or the battery to be supplied should rise to 57V and higher for any reason, the generator switches off immediately.
The output voltage of the generator is reduced when the maximum current is exceeded and can be lower than 48V, but if it gets too low, it is recognized as a short circuit and the generator is switched off immediately.
It is normal for the red LED to light up while charging at maximum current. This only means that the maximum output current of the generator has been reached.
PROTECTION IN THE EVENT OF LOW FUEL OR ENGINE OIL
If the fuel is used up, the engine stops.
If the oil level is too low (yellow LED lights up), the engine stops immediately.
If the starting conditions are met (the battery voltage is below 47.5-48V in AUTO mode or EXTERNAL CONTROL contacts are short-circuited in EXTERNAL CONTROL mode), the engine tries to start 5 times and if it doesn't work, an error message appears (red LED flashes).
EASY SERVICE
The generator does not have its own battery and is started by the battery to be supplied. The battery to be supplied usually has a capacity of several kWh and even with a low charge there is still more than enough energy to start the generator, even after several attempts to start it. This eliminates the need for regular maintenance of the generator's battery, as is customary with AC generators, for example, and increases the reliability of the emergency power supply when the generator is rarely used.
With the generator, however, care must be taken to ensure that the shelf life of the fuel is not exceeded. We recommend only using long-lasting petrol with an octane number of 90-95 as fuel, paying attention to possible deposits in the carburetor and draining them off in good time depending on the shelf life of the petrol.
It is also important to pay attention to the shelf life of the engine oil. This must be changed either every 12-18 months according to the manufacturer's specifications or every 50 operating hours.
The air filter should be replaced depending on how dirty it is.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
The direct current generator KS 48V-DC may only be operated with 48V batteries, which are listed in the table above. It is imperative to pay attention to the parameters of the entire power supply system. In systems where the 48V busbar is supplied exclusively by the inverter, it must be ensured that other DC power sources can be connected to the 48V busbar and that there are no faults in the controller (especially with energy management based on energy flows) of the plant caused.
DISCLAIMER:
These instructions can only be taken as a recommendation, are illustrative and must be adapted to the exact local circumstances and conditions during installation. The installation itself should be carried out in compliance with all standards and regulations. We take no responsibility for the wrong installations and their consequences.