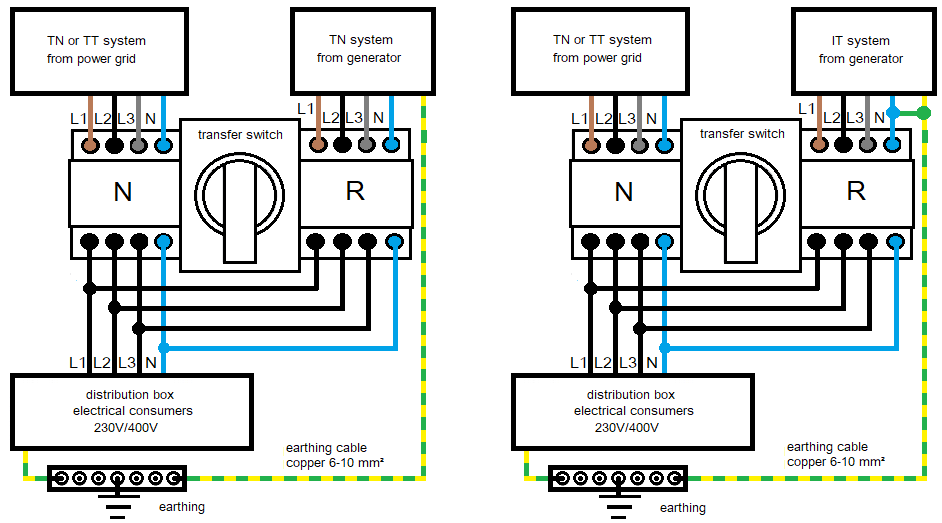
The house power supply from the public grid is made in the TN or TT system. The neutral conductor is grounded in both systems on the grid side. In the TN system, there is also a grounded PE conductor in the house, which must be connected to the house earthing. House earthing in the TT system is only intended for earthing internal power consumers and must not be connected to the neutral conductor from the public grid. With the TN system, a distinction is made between TN-C and TN-S systems.
The switchover of the power supply of the electricity consumers entitled to backup power in a house must take place at all poles in accordance with the VDN guideline for the planning, construction and operation of systems with backup power generators. All external conductors and the neutral conductor from grid must be safely separated.
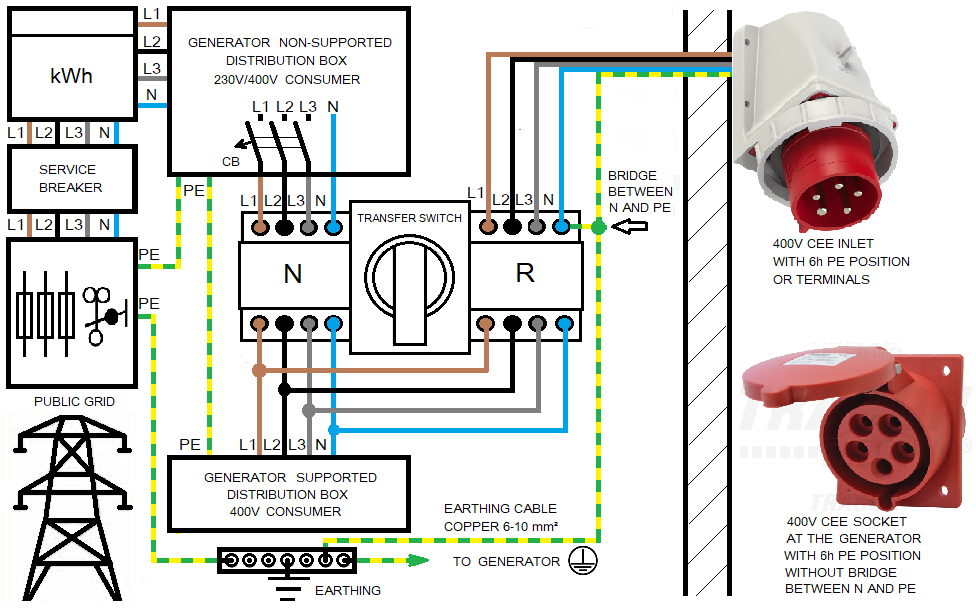
A TN system must be built on the diesel or gasoline generator side so that the supply of electricity consumers entitled to backup power continues to take place with the grounded neutral conductor after switching to emergency power:
Backup power supply must be designed in such a way that even an electrotechnical layman can use the generator safely without endangering himself or those involved.
For this reason, the backup power generators that are not permanently installed with Schuko sockets and CEE sockets with a 6-hour PE position must not be converted to a TN system by placing a bridge between N and PE on the generator site. We recommend setting this jumper on the transfer switch in the house so that a TN system is only created after the gasoline generator has been connected to the house and operation with the bridged N and PE is prohibited without grounding.
In the case of diesel or gasoline generator with an IT-TN switch, there are switches installed at the factory which, when switching from IT to TN, deactivate the Schuko sockets and CEE sockets with 6h PE position on the generator and activate the generator output to the CEE socket with 1h PE position use the bridge between N and PE. This prevents an electrotechnical layman from connecting individual power consumers directly to the generator and operating them without grounding, which would be operation in the IT system with the 1st error (leakage between an active line and the generator housing).Operating the generator with an internal bridge between N and PE without grounding can be life-threatening and is prohibited!
This is how the building the backup supply from a generator with an IT-TN switch, according to DIN 14092 and DIN VDE 0100-551 Supplement 1:
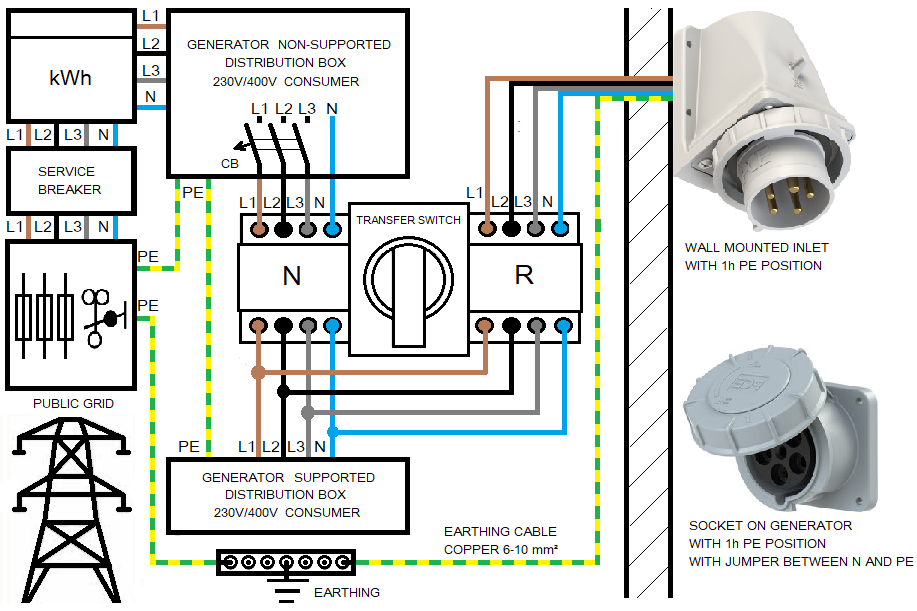
The gasoline or diesel generator is earthed via the PE pin in the CEE socket. The cable must be of sufficient cross-section to comply with local regulations regarding the minimum cross-section of the earthing cable. If this is not the case, the generator must be earthed separately.
Backup power connection on the building side from the diesel or gasoline generator with the bridge between N and PE must be made via the CEE inlet with 1h PE position. Alternatively, the building connection line can be connected via terminals. The PE pin in the power inlet or PE line from the connection cable must be connected to house earthing. Cables CEE 400V plug with 1h PE position to CEE 400V socket with 6h PE position are not permitted.
A certain contradiction can be found in the recommendation to install in the diesel or gasoline generator an RCD as protection against accidental contact. This is supposed to protect those involved against electric shock when touching the damaged cable on the route from the generator to the house. However, the tripping current of an upstream residual current device (RCD) to the downstream residual current device must be at least 3:1. Since further RCDs have to be installed in the building power distribution according to regulations, it is said that the residual current circuit breaker built into the generator must have the tripping current of 100 mA or more. However, only RCDs with a tripping current of no more than 30 mA can be used to protect people, because higher current intensities can be deadly. According to DIN VDE 0100-410, final circuits outdoors must be protected by RCDs with a tripping current of no more than 30 mA. However, the connection between the generator and the house does not belong to the final circuits. So the use of a residual current protective device in the generator for the house backup power supply remains questionable.
Power cables for a house power backup must have double insulation and must be checked for possible damage before each use in order to avoid a possible electric shock!
Switching devices are often installed with the CEE 400V inlet with the 6h PE position:
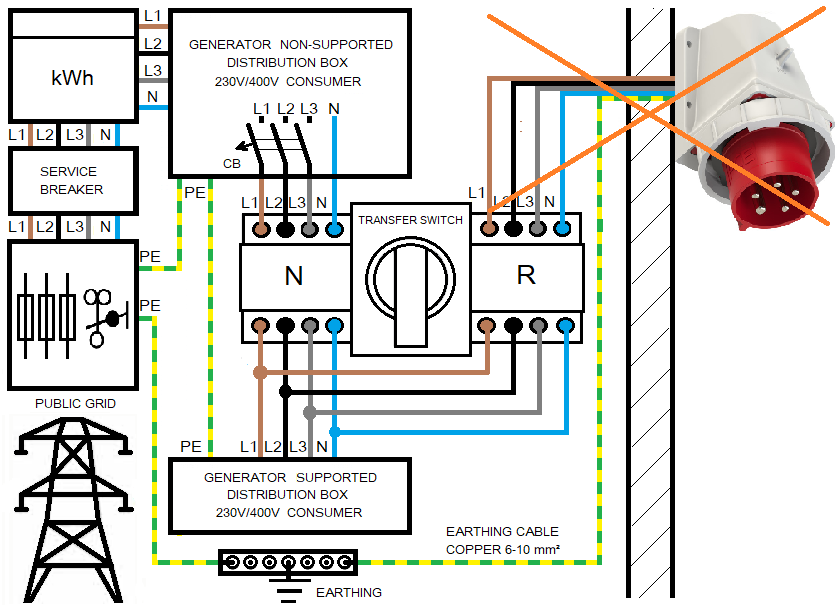
Such an installation can lead to an electrotechnical layman unknowingly supplies the house in the IT system directly from a mobile generator, without installing the necessary protection devices and without paying attention to the characteristics of the generator. Under certain circumstances, this can be life-threatening and also lead to damage to the equipment to be supplied.
Most backup power diesel or gasoline generators on the market are not suitable for unbalanced loads and in such a case the 400V socket should only be used for three-phase consumers that load all 3 phases symmetrically and not for a complete house power supply.
If a gasoline or diesel generator has an extra 400V socket for the house power supply with a 1h PE position, then it is suitable for unbalanced loads and for a 3-phase house power supply.
If a diesel or gasoline generator with the 400V socket with a 6h PE position is suitable for unbalanced loads, you have to ask the manufacturer separately if this is not clearly stated in the description.
It is always important to pay attention to sensitive electronic power consumers, which can be damaged when operated by a conventional generator.
You can find more about this in our information material at: https://koenner-soehnen.com/house-backup-power-supply-list/generators-and-electronics
The fact that most backup power generators on the market do not have an IT-TN mode selector switch and no CEE sockets with a 1h PE position does not mean that they are not suitable for home backup power supply. For example, generators with inverter technology are all 1-phase generators and do not have CEE sockets with a 1h PE position, but are designed for domestic use and are even suitable for sensitive electronic power consumers.
Here is the recommended connection plan for home power supply with a 230V generator with inverter technology in accordance with the VDN guideline for the planning, construction and operation of systems with emergency power generators:
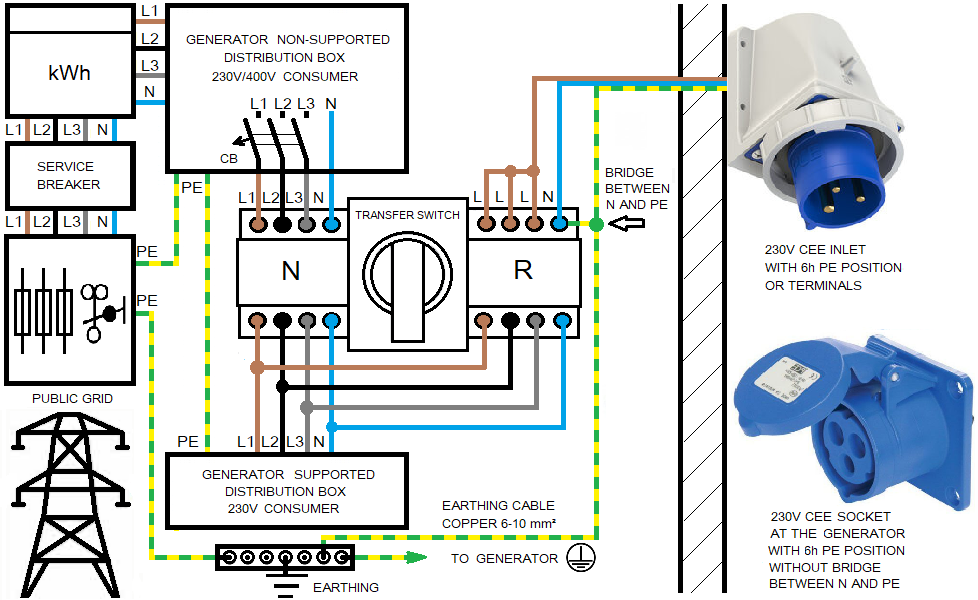
The diesel or gasoline generator itself remains as an IT system in such a connection scheme, but becomes part of the TN system as soon as it is connected to the house. This prevents incorrect use of the generator by an electrotechnical layperson.
The neutral conductor of the generator is only earthed in the house by a bridge between N and PE on the transfer switch. In this way, a TN system is created on the backup power side and it has no impact on normal power supply from the DSO grid.
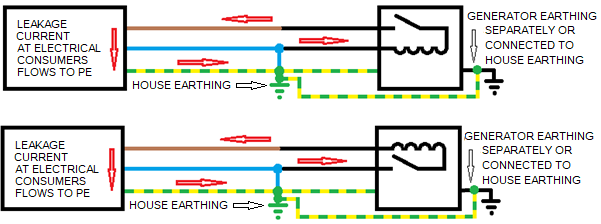
Course of the possible short-circuit currents in the case of leakage in the power consumer:
Short-circuit currents in the event of a leakage in the generator:
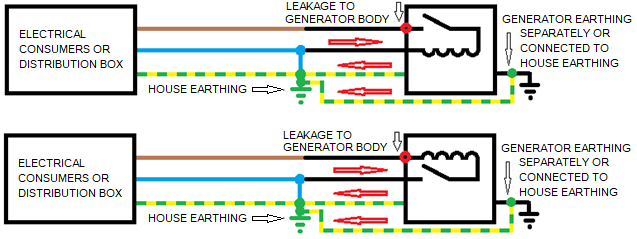 In contrast to the house backup power supply with a diesel or gasoline generator with the socket with 1h PE position, the generator must always be earthed separately via its earthing screw so that the housing of the generator is also protected in the event of a possible fault in the PE line to the house and a leakage in the generator has no life-threatening potential. The generator can be earthed both via the main earthing bar in the house and via its own earthing.
In contrast to the house backup power supply with a diesel or gasoline generator with the socket with 1h PE position, the generator must always be earthed separately via its earthing screw so that the housing of the generator is also protected in the event of a possible fault in the PE line to the house and a leakage in the generator has no life-threatening potential. The generator can be earthed both via the main earthing bar in the house and via its own earthing.
The power cable from the generator to the house must be checked for damage before each use. The generator does not have a built-in RCD!
When power supplying the house with a conventional gasoline generator, we recommend using an ohmic load to dampen harmonics caused by peak current consumption of the electronic consumers.
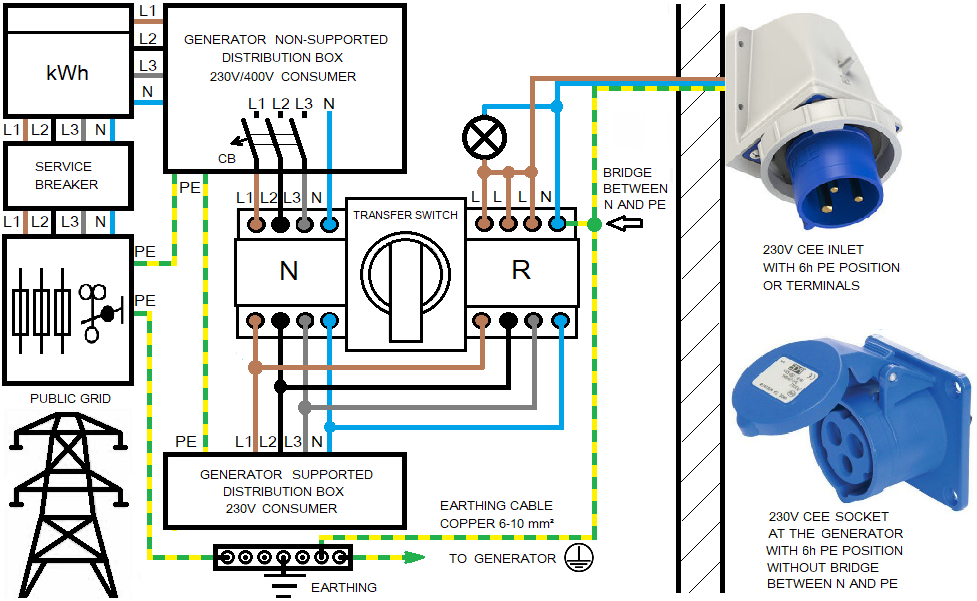
The ohmic load loads the parts of the sine curve of the voltage that are not loaded by non-linear electronic current consumers and thereby dampens the harmonics.
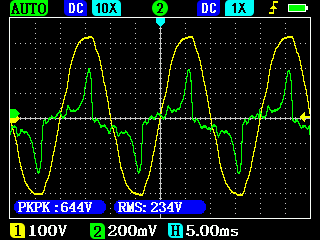
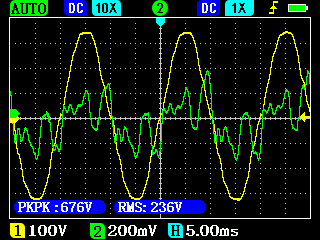
Voltage (yellow) and current (green) from a conventional generator under electronic load with and without ohmic load (100W light bulb):
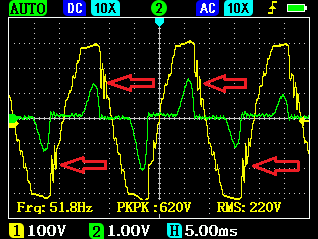
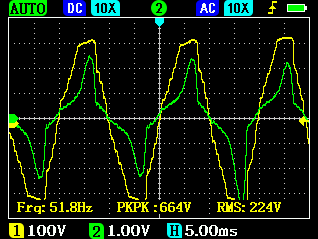
The interfering transient processes marked with the red arrows on the left picture are dampened by the ohmic load present in the circuit.
A 230V backup power generator can be used to supply all 230V power consumers that are entitled to backup power and were originally supplied from 3 different phases for the purpose of load distribution in the DSO grid.
Electricity consumers such as the electric stove, powerful instantaneous water heaters, electric boilers etc. are connected to 3-phase only for the purpose of load sharing in the DSO network and are in fact 230V electricity consumers that can be supplied by a 230V generator. However, these must not be operated with more than a third of the total power in order to avoid overloading the neutral conductor.
The ohmic load does not help with devices with power control via phase cut control, as this can lead to an extremely non-linear load on the sine wave with high currents and its deformation!
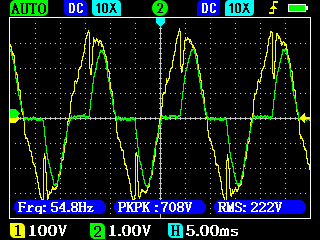
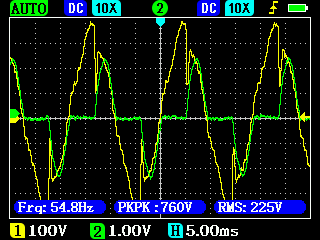
The electricity collection of a house usually has a complicated character:
The 3-phase generators, which are not suitable for unbalanced loads, are not to be used for a complete house power supply, but only for the backup power supply of the insensitive three-phase consumers in the house, which load all 3 phases symmetrically.
These are usually not sensitive and the use of ohmic loads is not necessary.
There are also 3-phase gasoline generators (or diesel generators) on the market that are only partially suitable for unbalanced loads. Even if the AVR regulates the excitation of each individual phase with an extra pulse, it is possible that the fast-running rotor is still magnetized enough to excite the next, after the more heavily loaded phase, lightly loaded phase to such an extent that the connected load suffers overvoltage damage.
Brief overview of the wall inlets for home backup power supply with mobile power generators
A house backup power supply should be implemented in such a way that even an electrotechnical layman cannot do anything wrong. No special versions of cables with internal bridges etc. that can be used incorrectly elsewhere may be used.
 | CEE 400V wall device plug with 1h PE position is used according to DIN VDE 0100-551 supplement 1 for a complete building backup power supply with mobile power generators. Accordingly, the power generator should have a CEE 400V socket with 1h PE position and a bridge between N and PE. These power generators are usually suitable for unbalanced loads, so that an asymmetrical load from mixed 230V and 400V power consumers is possible. Only the cable for backup power supply of the building can be connected to such a socket. |
 | CEE 230V inlet with 6h PE position is used for the backup power supply of 230V power consumers. The backup power generator must not be modified. Do not set bridges between N and PE in the generator! The bridge between N and PE is only set in the building. The cable to the building is considered the generator output and the TN system is only created when the generator is connected to the building. The generator remains as an IT system and can be used mobile. Only a 230V generator can be connected to such a socket, so that even an electrotechnical layman cannot do anything wrong. |
 | CEE 400V inlet with 6h PE position is used for the backup power supply of three-phase consumers that load all 3 phases symmetrically. No other power consumers may be supplied via this inlet! Do not set bridges between N and PE in the generator! The bridge between N and PE is only set in the building. The cable to the building is considered the generator output and the TN system is only created when the generator is connected to the building. The generator remains as an IT system and can be used mobile. Only a 3-phase generator can be connected to such a socket, so that even an electrotechnical layman cannot do anything wrong. |
In the case of a house backup power supply from the 230V diesel or gasoline generator with a Schuko socket, it is permissible to use a Schuko plug to 230V CEE connection cable. The Schuko plug can be reversed on the generator without affecting L and N in the house, since the N conductor is only earthed in the house. No adapter cables with internal bridge may be used, which an electrotechnical layman could use incorrectly elsewhere! Any adapter cables 400V to 230V etc. are not permitted for a building power supply.
L1, L2 and L3 in the CEE 400V inlet must not be bridged. If in your case a CEE 400V inlet with 6h PE position was used for a complete house feed, this installation has to be modified.
The generator for backup power of the house should be chosen taking into account its characteristics and the characteristics of consumers, since the wrong choice of generator can harm both consumers and the generator itself. Könner & Söhnen gives only general recommendations for the use of its generators.
Disclaimer:
These instructions can only be taken as a recommendation, are illustrative and must be adapted to the exact local circumstances and conditions during installation. The installation itself should be carried out in compliance with all standards and regulations. We take no responsibility for the wrong installations and their consequences.